Technical Background
Bridgestone have many superior generic technologies with regard to conveyor belts. We implement these technologies to develop superior products which fully satisfy our customers’ needs.
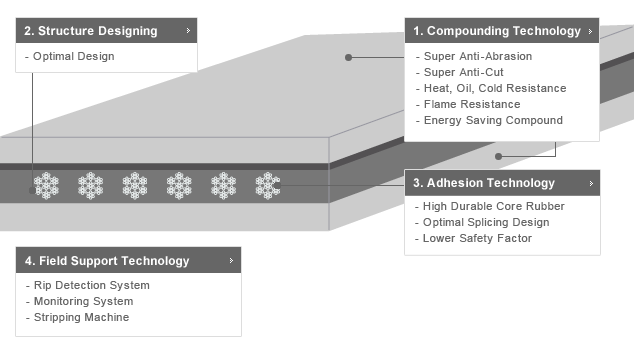
1. Compounding Technology
Rubber compounding technology for many products including Conveyor Belts is a fundamental technology to control the product performance.
The superior rubber compounding technology is essential for developing high durability rubber such as cut resistance, wear resistance and energy saving rubber.
Being the world’s leading rubber company, Bridgestone will continue to maximize and effectively utilize the resources to actively development and improvement of the rubber formulation for conveyor belt from other products technology.
Rubber Development Applying to Tire Technology
Life of a typical conveyor belt is dependent on top cover wear and cut damage – the same factors which influence the tire life. This fact has given rise to a common philosophy for rubber development.
Bridgestone industrial products department develops durable rubber for Conveyor Belts and exchanges the know-how with the tire department.
In addition, we also develop energy saving belt in cooperation with the tire department to achieve energy saving and further CO2 reduction.
High Durable Rubber Technology for High Market Demand
Conveyor Belts are used under various conditions. Thus, it is essential to develop the most suitable rubber compound for each individual conveyor line.
Optimum rubber combination study is done on a daily basis by comparing the collected field data and the laboratory data.

2. Structural Technology
As the steel cord and fabric act primarily as tensile members in the middle layer inside the conveyor belting, it is very important that these tensile members are very effectively adhered to the top and bottom covers – and to the inner rubber inside the belting. For this reason the so-called “core rubber” compound inside the belting is also highly critical for the overall structural critical integrity and long-term performance of the belting.
We are continuously designing and proposing the best belt specification for each individual application to ensure customer satisfaction.
3. Test Equipment
Bridgestone owns different types of test equipment simulating the belt usage under various conditions.
This equipment helps us establish the optimum belt design for each application.

4. FEM Technology
Bridgestone is applying FEM analysis using belt operation environment and belt structure for design optimisation purposes.
The FEM model has enabled a simpler evaluation process and a speedy product development according to customers’ needs.
5. Adhesion Technology
Before the conveyor belt is taken into operation, its both ends have to be joined/spliced together. At the splice, the rubber provides the adhesion to the carcass to safely manage the generated tensile forces of the conveyor system.
Therefore, a high level of adhesion between the carcass and the rubber is required. Optimum rubber selection and best splice design can improve the reliability of a splice.

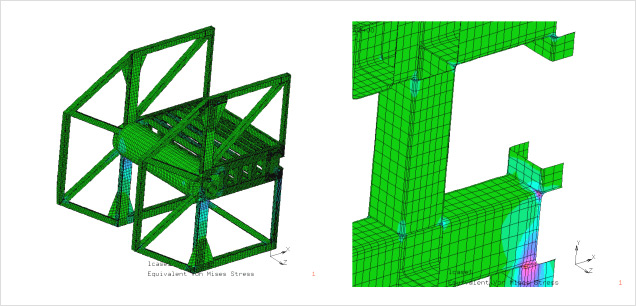
Stress Analysis for Optimization of Splice Design
To achieve a high level of durability, we select the best rubber for excellent adhesion strength and fatigue resistance and the best suited splicing design for our steel cord Conveyor Belts.
Bridgestone have introduced stress analysis technology. By combining the analytical and evaluation techniques, Bridgestone have achieved an optimum design for producing durable steel cord belts.
Stress Analysis
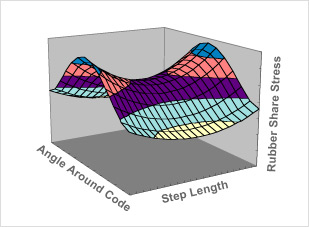
The stress can be minimized with optimum rubber selection and best splice design
Analytical Technique
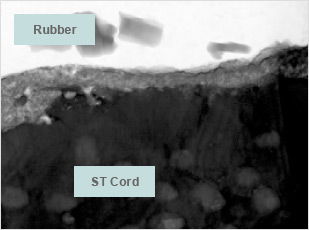
* Scale 1:300,000
Bridgestone uses the latest analytical technique to realize world highest level of steel cord & rubber adhesion strength
6. Field Support Technology
Bridgestone also develop and offer a variety of peripheral devices which can assist with your productivity improvement.
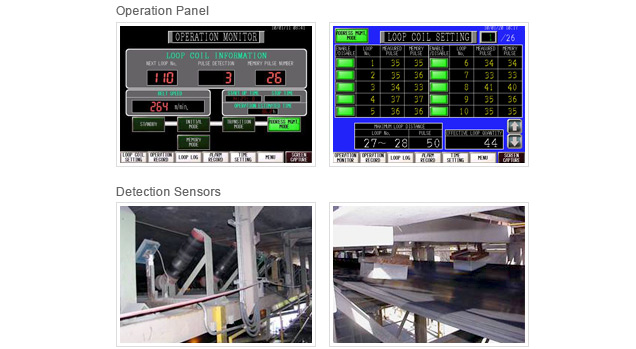
Longitudinal Split Detector – Rip Sensor
The system locates longitudinal splits in the belt by detecting whether loop coils embedded in the bottom cover rubber of the belt have been ripped.
For more information, click here.